Launching a startup is a race against time, capital, and uncertainty. Founders must turn an idea into a working product before the runway runs out — and ideally, reach product-market fit before competitors catch up. That’s why more startups today are leveraging outsourcing not just to save money, but to accelerate growth, access top tech talent, and reduce execution risk.
According to Statista (2024), the global IT outsourcing market surpassed $430 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $777 billion by 2028. For startups, this isn’t a corporate fad — it’s a survival tactic.
In this article, we’ll explore how outsourcing can help early-stage startups move from MVP to product-market fit faster, the key models available, when to use each, and how to avoid the common pitfalls.
1. Why Speed Matters: From Idea to Validation
Every startup founder knows: the faster you validate your idea, the higher your odds of survival.
An MVP (Minimum Viable Product) is the first tangible step — a simplified version of your product that tests core assumptions with real users.
But building even a “simple” MVP can be resource-intensive: hiring engineers, setting up infrastructure, and finding designers can take 3–6 months. That’s where outsourcing becomes a strategic accelerator.
Outsourcing enables founders to:
- Build and launch an MVP in weeks, not months.
- Save 30–50% of development costs (Devico.io, 2024).
- Focus on customers, investors, and growth — instead of recruitment.
As Pulsion Technology (2024) puts it, “Startups that outsource their MVP development often reach market validation twice as fast.”
2. The Main Outsourcing Models for Startups
Not all outsourcing is created equal. Startups can choose from several engagement models depending on their goals, resources, and stage of development.
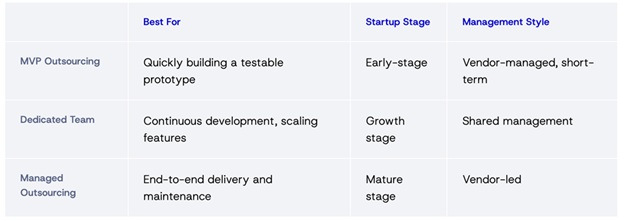
MVP Outsourcing
Ideal for idea-stage startups that need to test hypotheses quickly. You provide requirements and vision — the vendor builds the MVP under a fixed budget and timeline.
Pros: Fast, cost-effective, minimal overhead.
Cons: Limited flexibility for mid-project pivots.
Dedicated Team
Your vendor provides a stable, long-term team that integrates with your company culture and processes.
Pros: Continuity, better knowledge retention, scalable capacity.
Cons: Requires active management and clear leadership on your side.
Managed Outsourcing
A full-service model where the vendor handles everything — from architecture and UX to maintenance.
Pros: Hands-free and predictable.
Cons: Less control and higher long-term cost.
3. The Numbers: Why Startups Outsource
Several recent studies highlight why outsourcing has become a default strategy for startups:
- Startups can reduce development costs by up to 40% when outsourcing (Aalpha, 2024).
- The average time-to-MVP is reduced by 2–3x compared to in-house development (Industrial Innovation, 2024).
- 82% of successful startups began with a basic MVP built by an external team (InnovaLabs, 2024).
- Startups that used hybrid or dedicated-team models had higher post-MVP survival rates (67%) than those with full in-house teams (52%) (Techstack Digital, 2024).
The takeaway? Outsourcing isn’t about saving pennies — it’s about buying time, agility, and expertise.
4. Pros and Cons for Founders and Investors
The Advantages
Speed to Market: No months-long recruitment cycles. Start coding next week.
Runway Preservation: Lower operational and hiring costs.
Access to Top Talent: You can get senior engineers and product managers from specialized vendors.
Focus on Core Value: Founders can dedicate attention to fundraising, customer validation, and marketing.
Scalability: You can ramp up or down based on investor milestones.
The Risks
Communication Barriers: Time zone and cultural differences can slow decision-making.
Quality Gaps: Without tight oversight, code quality and UX may suffer.
Loss of Control: Vendors might optimize for delivery speed rather than long-term scalability.
IP Ownership: Poor contracts can cause disputes over code or design ownership.
Hidden Costs: Scope changes and technical debt can inflate expenses by 20–30% (Gartner, 2024).
Pro tip: The key to mitigating these risks lies in vendor selection, clear contracts, and agile governance.
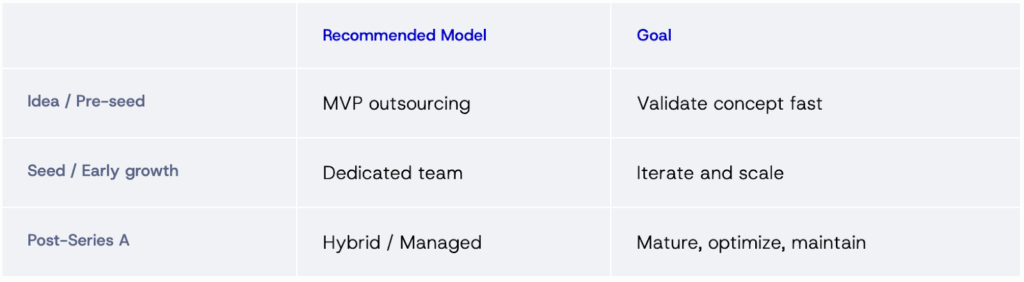
5. When Should a Startup Outsource?
Outsourcing makes sense if:
- You have a validated idea but lack in-house technical capacity.
- You’re on a tight runway and need to show progress before the next funding round.
- You need niche expertise (e.g., AI, fintech security, or blockchain).
- You want to prototype multiple ideas before committing to one.
However, you should avoid outsourcing if:
- Your product involves deep proprietary tech or intellectual property.
- You have a strong in-house team with product-market experience.
- Your product requires tight user feedback loops that need immediate iteration.
Decision framework:
6. How to Build an Effective Outsourcing Partnership
To succeed with outsourcing, treat your vendor as a strategic partner, not a contractor.
Best practices:
1. Define MVP scope precisely — focus on core value, not “nice-to-haves.”
2. Choose a vendor with startup DNA — not just technical capacity.
3. Set agile governance — weekly demos, sprint reviews, and KPIs.
4. Ensure transparency — shared tools (Jira, Slack, Notion) and clear reporting.
5. Protect your IP — NDA, source-code access, and IP transfer clauses.
6. Plan the transition — ensure post-MVP knowledge transfer or internal team integration.
Example: A startup in Berlin partnered with a Ukrainian development firm to build its MVP in 12 weeks. The collaboration resulted in a successful seed round, and the same vendor later became their dedicated team for scaling. This continuity saved the startup ~35% in development costs and months of hiring effort.
7. The Investor Perspective
For venture capitalists, outsourcing can be a positive signal — showing that founders are resourceful, lean, and execution-focused.
However, investors look for:
- Proof of ownership of code and IP.
- A clear handover plan for when the startup scales.
- Evidence that outsourcing accelerated learning, not delayed it.
Outsourcing isn’t a shortcut; it’s a scaling lever when managed with discipline.
8. The Future of Startup Outsourcing
By 2028, more than 60% of startups are expected to use hybrid models — mixing internal leadership with external execution.
AI-driven communication tools, nearshore development, and agile vendor ecosystems are making global collaboration easier than ever.
Startups that master this hybrid agility will move from MVP to product-market fit faster — and with fewer burnouts and budget overruns.
9. Conclusion: Outsourcing as a Strategic Accelerator
Outsourcing isn’t about delegating — it’s about amplifying your startup’s capabilities.
Used wisely, it’s a tool for velocity, focus, and survival.
Whether you’re a founder validating your MVP or a VC evaluating a startup’s roadmap, the message is clear:
The right outsourcing partnership can be the difference between burning runway and building momentum.
Define your product vision.
Pick the right model.
Partner smart.
And get to product-market fit — faster.
Sources:
- Statista (2024). IT Outsourcing Market Size.
- Aalpha (2024). How to Outsource MVP Development in 2025.
- Devico.io (2024). Software Development Outsourcing Guide for Startups.
- InnovaLabs (2024). MVP Development Services Report.
- Gartner (2024). Outsourcing Cost Overrun Study.
- Pulsion (2024). Outsourcing Benefits for Startups.
Industrial Innovation (2024). On Outsourcing the MVP.

